Financial ServicesAI
The technical and operational path to agentic AI in financial services
Unlocking Agentic AI’s true value requires a sturdy foundation and careful evaluation to avoid unintended consequences,…
Read article

Hospitality & Entertainment Financial Services Assessment & Optimization
08/16/2022
by Sean Sims

You’ve got the perfect vacation planned down to the last detail – flights, hotels, restaurants, and family activities are booked. As soon as you leave work and vacation mode begins, the last thing on your mind will be how your payment card data will be handled during your trip. Thankfully, other people are thinking about that for you – merchants, service providers, card networks, and the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC). These bodies leverage PCI DSS requirements to help ensure your data is protected.
The Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) was created by Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover, and JCB to combat payment card fraud. They developed the PCI Data Security Standards (DSS), which applies to all businesses that process, store, or transmit payment card information and defines a set of requirements to ensure secure data handling.
The PCI DSS is constantly being reviewed and adjusted to ensure it adapts to current needs and new threats. In April 2022, PCI DSS v4.0 was released and merchants will have 2 years to adjust to these updated standards. At a very high level, the PCI SSC divides the DSS into the following areas:
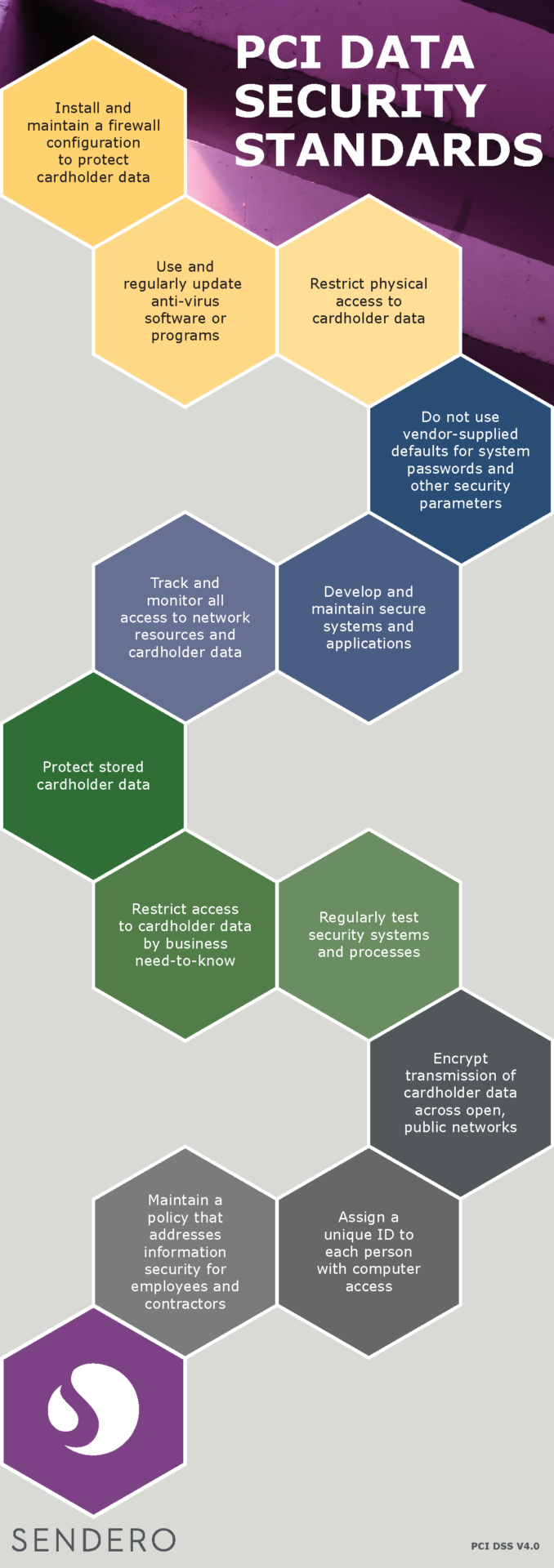
For each of these “big picture” requirements and best practices, the PCI DSS provides much more detailed, technical guidance. One of the nuances to the guidance comes from the fact that merchants are categorized into 4 different levels according to their payment card transaction level over a 12-month period. A Level 1 merchant (high transaction volume) will have the strictest, more scrutinized DSS requirements; a Level 4 merchant will have the most lenient requirements.
In the hospitality industry, a good reputation is correlated with success. Customers often look at online reviews, ask for word-of-mouth recommendations, or use their previous knowledge before choosing hotels, restaurants, or recreational activities. When a hospitality business chooses not to comply with the PCI DSS, they’re at risk of damaging that all-important reputation (and incurring hefty fines) if a data breach is incurred.
Unfortunately, the hospitality segment accounts for 40% of credit card breaches and credit card theft worldwide. In recent years, multiple major industry leaders announced substantial data breaches, including Marriott, MGM Resorts, and Choice Hotels. This can make customers think twice before handing over their payment card.
There are several reasons that the hospitality industry is highly susceptible to cyber attacks:
There are some key things merchants should keep in mind to better protect customers’ data:
With constant changes and advances in technology come added data security threats. The silver lining? Merchants, service providers, card networks, and the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) are actively working to identify and mitigate these threats so that you can use your payment card and enjoy your well-planned vacation.
Looking for help in navigating the newest set data security standards? Connect with one of our consultants using the form below.
Business insights
Financial ServicesAI
Unlocking Agentic AI’s true value requires a sturdy foundation and careful evaluation to avoid unintended consequences,…
Read article

Financial ServicesPlatform & Products
Weak financial systems integration slows growth in markets where speed and confidence matter most. Integration chaos…
Read article

Financial ServicesAI
Hyper-personalization is becoming a critical differentiator in financial services. AI and broader digital…
Read article
